Blog
Top 10 Benefits of Using LoRaWAN Sensors for Smart Cities and Agriculture
In an era where urbanization and agricultural efficiency are paramount, the integration of technology into these spheres is becoming increasingly vital. LoRaWAN sensors, known for their long-range connectivity and low power consumption, are emerging as game-changers in the development of smart cities and modern agricultural practices. With the ability to collect and transmit data over vast distances, these sensors facilitate real-time monitoring and automation, making them essential tools in optimizing resources and enhancing sustainability.
As Dr. Emily Johnson, a renowned expert in IoT applications for urban development, once stated, "LoRaWAN sensors are revolutionizing the way we understand and interact with our environment, paving the way for smarter, more efficient cities and agricultural practices." This sentiment encapsulates the transformative potential of this technology. By harnessing the advantages of LoRaWAN sensors, city planners and farmers can make data-driven decisions that not only improve operational efficiency but also contribute to a greener planet. As we explore the top 10 benefits of using LoRaWAN sensors, it becomes clear that they are not just a technological advancement but a pivotal element in fostering sustainable growth in both urban and rural settings.
Benefits of LoRaWAN Sensors in Enhancing Urban Infrastructure Efficiency
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) sensors are increasingly recognized for their role in enhancing urban infrastructure efficiency, driving the development of smarter cities. According to a report by the International Telecommunication Union, smart city technologies, including LoRaWAN, can improve energy efficiency in cities by up to 30%. These sensors allow for real-time monitoring of utilities, traffic, and environmental conditions, enabling city officials to make informed decisions that optimize resource allocation and reduce operational costs. For instance, real-time data from LoRaWAN sensors can be used to monitor waste levels in bins, leading to more efficient collection routes and reducing fuel consumption by an estimated 20%.
Moreover, the deployment of LoRaWAN sensors significantly improves urban resilience and sustainability. A study by ResearchAndMarkets indicated that smart city initiatives powered by IoT technologies like LoRaWAN could save cities approximately $4 trillion by 2030 through enhanced operational efficiency and reduced energy costs. This technology allows for predictive maintenance of public infrastructure, resulting in fewer service outages and longer lifespans for assets such as bridges, roads, and public transport systems. The ability to leverage data analytics from LoRaWAN networks not only fosters sustainability but also enhances the quality of life for residents through improved urban planning and responsive governance.
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Urban Infrastructure | Impact on Agriculture |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Enhanced Monitoring | Real-time data collection for environmental parameters. | Improved waste management and pollution control. | Better soil quality and crop health monitoring. |
| 2. Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs due to reduced infrastructure needs. | Reduces maintenance expenses for city services. | Minimizes resource usage and maximizes yield. |
| 3. Improved Connectivity | Seamless network for device communication. | Integration of city-wide IoT applications. | Connects farmers to market data effectively. |
| 4. Energy Efficiency | Low-power devices extend battery life. | Sustainable energy management in cities. | Energy-intensive farming processes are optimized. |
| 5. Data-Driven Decisions | Utilizes analytics for predictive insights. | Enhances public service efficiency. | Empowers farmers with actionable data. |
| 6. Scalability | Easily add sensors without major overhaul. | Adaptable to growing urban needs. | Can expand as farming operations grow. |
| 7. Increased Safety | Smart sensors improve public safety and emergency responses. | Helps monitor infrastructure health. | Monitors hazardous conditions in real-time. |
| 8. Environmental Protection | Helps track and reduce emissions. | Minimizes negative impacts on ecosystems. | Promotes sustainable farming practices. |
| 9. Community Engagement | Fosters participation in smart city initiatives. | Informs public on urban planning. | Encourages community-supported agriculture. |
| 10. Innovation Boost | Encourages development of new technologies. | Stimulates investment in urban tech solutions. | Promotes precision agriculture technologies. |
Role of LoRaWAN Sensors in Precision Agriculture and Crop Monitoring
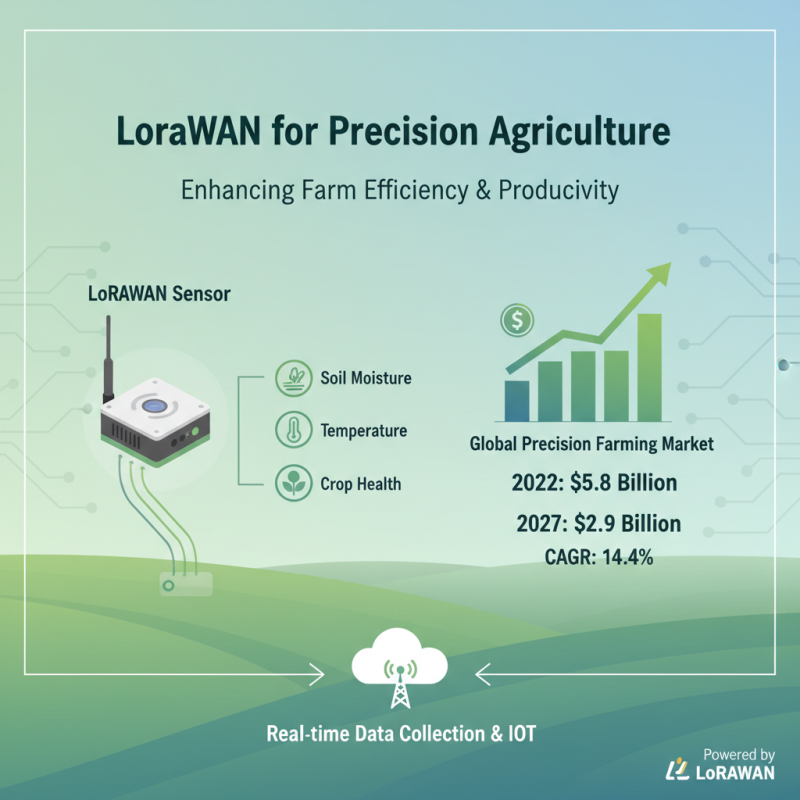
LoRaWAN sensors have emerged as a vital technology in precision agriculture and crop monitoring, significantly enhancing the efficiency and productivity of farming operations. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global precision farming market is projected to reach $12.9 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 14.4% from 2022 to 2027. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of IoT devices, including LoRaWAN sensors, which facilitate real-time data collection on a variety of parameters such as soil moisture, temperature, and crop health.
These sensors enable farmers to optimize their resource usage by providing data that helps in making informed decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest management. For instance, a study published by the International Journal of Agricultural Research indicated that farms employing precision agriculture techniques, including the use of LoRaWAN sensors, can achieve yield increases of up to 20% while reducing water usage by 30%. By implementing these technologies, farmers not only boost productivity but also contribute to sustainable practices that minimize environmental impact and conserve vital resources.
Impact of LoRaWAN on Reducing Operational Costs for Smart Cities
The integration of LoRaWAN sensors in smart cities is revolutionizing operational efficiency and significantly reducing costs. By enabling long-range communication with low power consumption, these sensors can facilitate real-time monitoring of various urban systems, from traffic management to environmental monitoring. This capability allows city planners to optimize the use of resources, leading to decreased energy consumption and reduced expenditure on infrastructure maintenance. For example, smart lighting systems equipped with LoRaWAN sensors can adjust their brightness based on pedestrian presence, thus saving energy and lowering utility bills.
Moreover, the data collected through LoRaWAN sensors helps municipalities make informed decisions based on accurate analytics. This data-driven approach enables cities to pinpoint inefficiencies or high-demand areas, addressing issues before they escalate into costly problems. For instance, water management systems can detect leaks early, preventing loss of resources and reducing the need for expensive repairs.
By enhancing the overall operational effectiveness of urban services and agriculture management, LoRaWAN technologies not only streamline processes but also foster a more sustainable and economically viable environment for both citizens and local governments.
LoRaWAN Data Insights for Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability
LoRaWAN sensors are becoming increasingly vital for environmental monitoring and sustainability in smart cities and agricultural settings. These low-power wide-area network devices facilitate extensive data collection across large terrains, significantly enhancing our ability to monitor environmental conditions in real time. According to a report by the International Telecommunication Union, the adoption of IoT sensors, including LoRaWAN, can improve energy efficiency by up to 30% in urban areas, illustrating the critical role of technology in fostering sustainable practices.
In agriculture, LoRaWAN sensors provide crucial insights into soil moisture levels, temperature fluctuations, and crop health, enabling farmers to optimize resource usage effectively. A study by Markets and Markets estimates that precision agriculture, driven by IoT technologies, could lead to a reduction in water consumption by up to 20% while simultaneously boosting crop yields by as much as 30%. This integration of data-driven insights promotes sustainable farming practices and ensures food security amidst growing concerns about climate change and resource scarcity. As cities and farms alike embrace these advancements, the potential for improved environmental monitoring and sustainable development becomes more tangible.
Top 10 Benefits of Using LoRaWAN Sensors for Smart Cities and Agriculture
This chart illustrates the top 10 benefits of utilizing LoRaWAN sensors in smart cities and agricultural practices, showcasing significant improvements in various areas such as data collection, sustainability, and resource management.
Integration of LoRaWAN Sensors for Improved Public Safety and Security
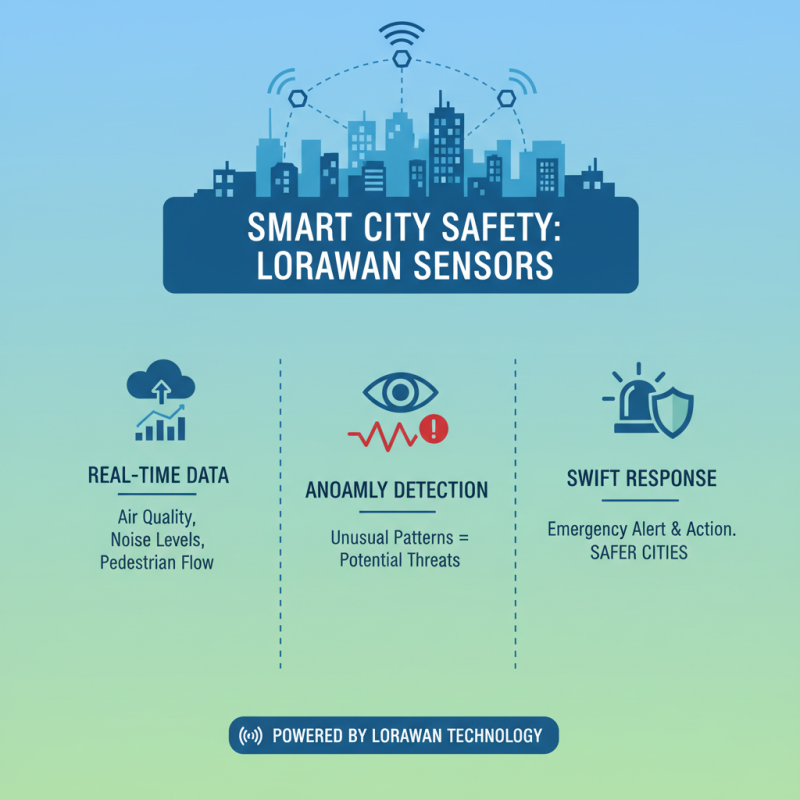
The integration of LoRaWAN sensors in urban environments plays a crucial role in enhancing public safety and security. These sensors provide real-time data collection capabilities, enabling city management to monitor various aspects such as air quality, noise levels, and pedestrian movement. By analyzing this data, authorities can detect unusual patterns that may signal potential safety issues, such as unrest in crowded areas or environmental hazards that could threaten public wellbeing. The proactive approach facilitated by LoRaWAN technology empowers cities to respond swiftly to emergencies, ensuring a safer environment for all residents.
Additionally, LoRaWAN sensors support the establishment of smart surveillance systems. Their long-range connectivity allows for widespread deployment across urban areas, connecting devices like cameras and emergency response tools. This creates a network that enhances situational awareness, enabling quicker response times and more coordinated efforts among emergency services. The improved communication between these systems also aids in crime prevention, as the data derived from sensor networks can be used to identify high-risk areas and allocate resources effectively. By leveraging the capabilities of LoRaWAN sensors, cities not only enhance security but also foster a sense of safety among their inhabitants.
Related Posts
-

10 Best Power Monitors to Optimize Your Energy Usage in 2023
-

Top Temperature Monitoring Solutions for 2025 You Need to Know
-
10 Essential Tips for Effective Tank Level Monitoring System Management
-

Top 2025 Power Monitoring Systems: How to Choose the Right One for Your Needs
-

Why You Need a Power Consumption Meter to Save Energy and Reduce Costs
-

Top 5 Power Monitoring Systems to Boost Energy Efficiency by 30% in 2023

