Blog
What is a Gas Meter? Understanding Types, Functions, and How to Read It
In the evolving landscape of energy consumption, understanding what a gas meter is, along with its various types and functions, has become increasingly important for consumers and businesses alike. According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), natural gas is projected to meet nearly 25% of the world's energy demand by 2025, underscoring the critical role that gas meters play in both residential and commercial sectors. Tracking usage accurately not only helps in billing but also promotes efficient energy consumption, paving the way for a sustainable energy future.
Expert in the field, Dr. Amelia Thompson, a senior researcher at the Energy Measurement Institute, emphasizes the significance of proper gas meter usage: "An accurate gas meter is essential for ensuring fair billing and efficient resource management in our households and industries." This statement highlights the profound impact that gas meters have on our daily lives and the importance of understanding how to read and interpret them effectively. As we delve deeper into the types of gas meters available, their functions, and the practical steps to read them, we will uncover the essential knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of gas consumption in an informed manner.

What is a Gas Meter and Its Importance in Energy Measurement
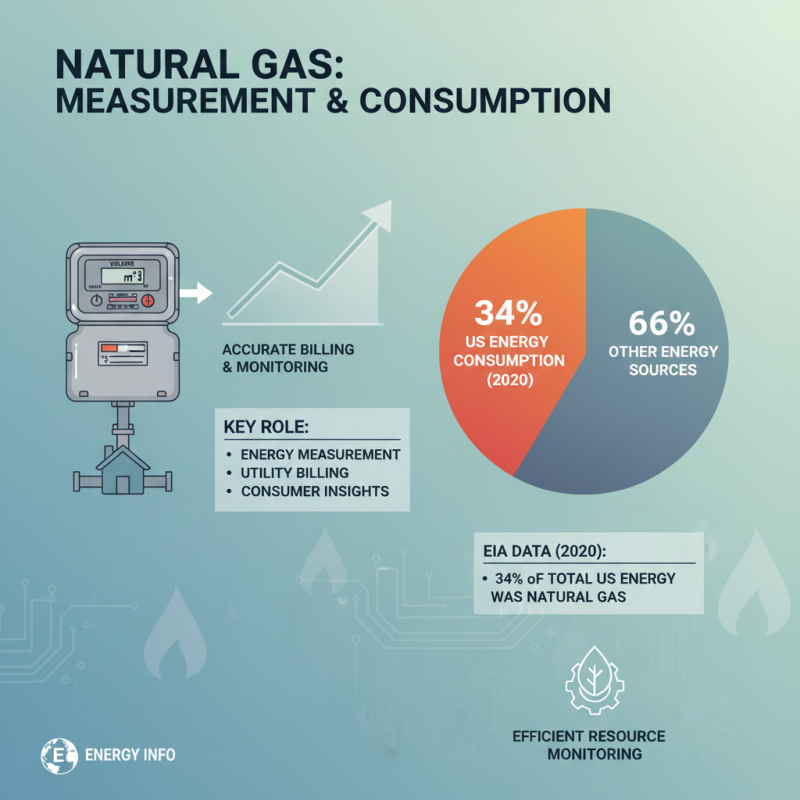
A gas meter is an essential device that measures the volume of gas consumed by residential and commercial buildings, playing a vital role in energy measurement. These meters ensure accurate billing by utility companies and enable consumers to monitor their gas usage effectively. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), in 2020 alone, natural gas accounted for about 34% of total U.S. energy consumption, highlighting the need for efficient monitoring and management of this vital resource.
The importance of gas meters extends beyond billing; they also serve as a tool for promoting energy efficiency. By providing consumers with detailed information about their gas usage, gas meters help identify patterns and opportunities for savings. The International Energy Agency (IEA) emphasizes that improved gas metering can lead to a significant decrease in energy waste, which is crucial in the fight against climate change. As gas consumption continues to rise, the role of gas meters in ensuring accurate measurements and fostering sustainable energy practices becomes increasingly essential.
Types of Gas Meters Used in Residential and Commercial Settings
Gas meters are essential devices for measuring the volume of gas consumed in residential and commercial settings. These meters help utility companies monitor usage and bill customers accurately. In the industry, two primary types of gas meters are commonly used: diaphragm meters and rotary meters. Diaphragm meters are predominantly used in residential settings due to their reliability and accuracy for lower flow rates, typically up to 250,000 BTU/h. According to the American Gas Association, approximately 80% of residential gas systems utilize diaphragm meters.
On the other hand, rotary meters are favored in commercial and industrial applications, where higher flow rates are necessary. These meters can handle volumetric flows exceeding 1,000,000 BTU/h, making them ideal for larger facilities. A report from the Gas Technology Institute indicates that rotary meters account for nearly 20% of the gas measurement market, reflecting their importance in environments that require precise gas management and control.
Understanding the different types of gas meters is crucial for both consumers and service providers. Accurate readings provided by these meters not only ensure correct billing but also enhance energy efficiency and safety. The ongoing advancements in gas meter technology, including smart meters, are also paving the way for improved data collection and real-time monitoring, which can lead to better resource management in both residential and commercial sectors.
Gas Meter Types and Usage in Residential vs. Commercial Settings
Key Functions and Features of Modern Gas Meters
Modern gas meters are essential devices that play a crucial role in the accurate measurement of gas consumption in residential and commercial settings. These meters are designed to provide real-time data on usage, ensuring that consumers are billed accurately based on their actual consumption patterns. One key function of modern gas meters is their ability to record usage digitally, allowing for enhanced readability and reduced human error associated with manual readings. Many contemporary models feature an LCD display that presents clear information, making it easier for users to monitor their gas consumption regularly.
Another significant feature of modern gas meters is the implementation of smart technology. Smart meters can communicate directly with the utility provider through wireless networks, facilitating remote readings and improving the efficiency of billing processes. This technology also allows for better energy management, as users can track their consumption trends over time. Some smart meters come equipped with alerts and notifications, helping users identify any unusual spikes in usage that may indicate leaks or other issues. Overall, the advancements in gas meter technology enhance user experience and promote energy efficiency in gas consumption.
What is a Gas Meter? Understanding Types, Functions, and How to Read It
| Type of Gas Meter | Function | How to Read | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diaphragm Gas Meter | Measures volume of gas used | Read from dials or digital display | High accuracy, durable construction |
| Rotary Gas Meter | Measures flow of gas using rotary mechanism | Digital readout or mechanical dials | Compact design, designed for high flow rates |
| Smart Gas Meter | Tracks gas usage and transmits data | App or web interface for reading | Remote monitoring, energy usage analysis |
| Ultrasonic Gas Meter | Measures gas flow using ultrasonic waves | Digital display, automated data logging | High precision, no moving parts |
| Coriolis Gas Meter | Measures mass flow of gas | Digital readout with mass flow results | Highly accurate, suitable for a range of applications |
How to Accurately Read a Gas Meter: A Step-by-Step Guide
Reading a gas meter accurately is essential for monitoring gas consumption and managing utility bills effectively. Gas meters typically have a series of dials or a digital display that indicates the total amount of gas used, measured in cubic feet or meters. When reading a traditional dial meter, start from the leftmost dial and move to the right. It's crucial to record the numbers carefully, noting that the needle may point between two numbers. In such cases, always write down the lower number; if the needle points directly at a number, check the following dial to see if it's passed the last number, which may affect your reading.
For digital meters, the process is simplified as the display shows a direct reading, eliminating the need for interpretation. According to industry reports, accurate readings can significantly impact energy efficiency, as they allow consumers to track their usage patterns and make informed decisions about energy consumption. A study from the American Gas Association revealed that residential customers who regularly monitor their gas meter readings are more likely to reduce their usage by up to 15% over time. This proactive approach not only promotes energy conservation but also helps households understand trends in gas consumption, ultimately leading to more sustainable energy practices.
Understanding Gas Meter Data: Insights Into Consumption Patterns
Gas meter data plays a crucial role in understanding consumption patterns and managing energy use efficiently. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), residential natural gas consumption can vary widely depending on factors such as season, home size, and energy efficiency measures. For instance, a typical household might use between 50 to 150 therms per month during winter months, while summer usage can drop significantly, often falling below 30 therms. This variability provides insights into both typical consumption and periods of increased demand.
Analyzing gas meter readings over time can reveal important trends in usage. Research from the International Energy Agency indicates that homes equipped with smart gas meters can show a reduction in consumption by up to 10% due to enhanced consumer awareness and more efficient practices prompted by real-time data feedback. Additionally, understanding daily and seasonal consumption patterns helps utility companies better forecast energy needs and manage supply, ultimately contributing to a more stable and efficient energy market.
Regularly monitoring gas meter data can empower consumers to adjust their habits, thereby potentially lowering their bills and reducing their overall carbon footprint.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Onset Data Loggers for Accurate Temperature and Humidity Monitoring
-

Why You Need a Power Consumption Meter to Save Energy and Reduce Costs
-

Top 2025 Digital Data Logger Features: What You Must Know!
-

2025 Top 10 Data Loggers You Can't Miss: Ultimate Buying Guide
-
10 Essential Tips for Effective Tank Level Monitoring System Management
-

Top 5 Power Monitoring Systems to Boost Energy Efficiency by 30% in 2023

