Blog
How to Use LoRaWAN Sensors for Efficient IoT Solutions
In recent years, the Internet of Things (IoT) has seen unprecedented growth, with a projected 30 billion connected devices by 2025, according to a report by IoT Analytics. Among the various enabling technologies, LoRaWAN sensors have emerged as a critical component for efficient IoT solutions. These sensors provide long-range communication with low power requirements, making them ideal for applications ranging from smart cities to precision agriculture. Industry experts, such as Dr. Emily Johnson, a leading researcher in the field, have highlighted the importance of LoRaWAN sensors, stating, "The versatility and efficiency of LoRaWAN technology are transforming how we gather data and monitor our environments."
Furthermore, data from the LoRa Alliance indicates that the adoption of LoRaWAN technology in various sectors has increased by over 40% annually, reflecting the growing recognition of its potential. As businesses and municipalities seek to implement more sustainable practices and leverage real-time data analytics, the role of LoRaWAN sensors in facilitating efficient IoT solutions cannot be overstated. These sensors not only provide vital data but also contribute to cost reductions and enhanced operational efficiency across diverse applications. The integration of LoRaWAN technology in various industries is paving the way for smarter decision-making and resource management, ushering in a new era of connectivity and innovation.

Understanding LoRaWAN Technology and Its Role in IoT
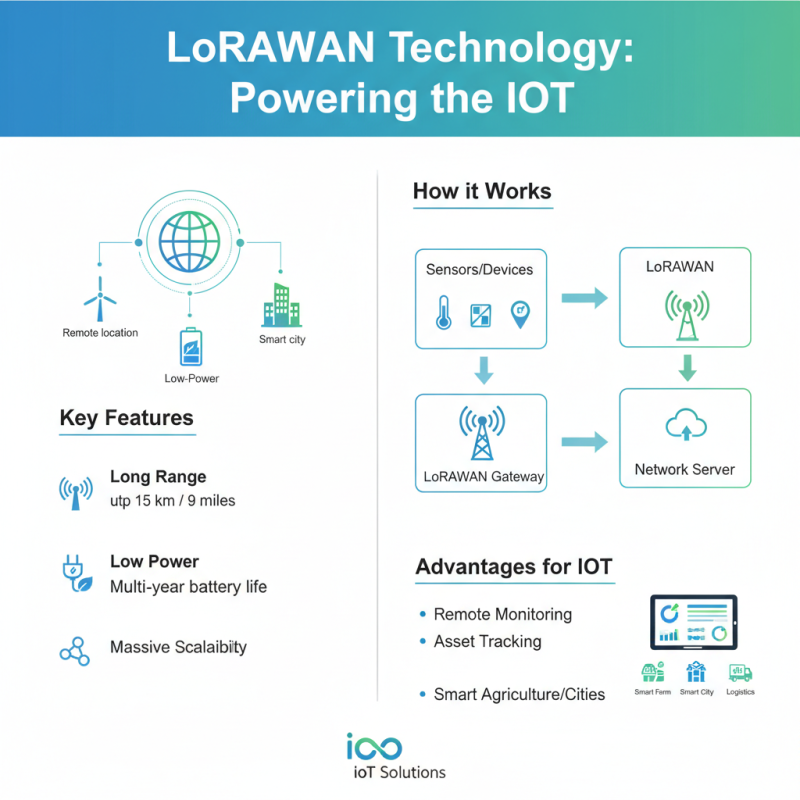
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) technology has emerged as a pivotal component in the landscape of the Internet of Things (IoT). Designed for low-power, long-range communication, LoRaWAN enables devices to transmit data over significant distances while consuming minimal energy. This is especially advantageous for IoT applications where sensors are often deployed in remote locations and need to operate on limited battery power. The architecture of LoRaWAN facilitates the connection of numerous sensors to a single gateway, creating a scalable and efficient network capable of handling vast amounts of data generated by connected devices.
The role of LoRaWAN in IoT is particularly significant in applications such as smart city infrastructure, agricultural monitoring, and asset tracking. By providing robust connectivity in environments typically challenging for traditional cellular networks, LoRaWAN allows for real-time data collection and analysis. This capability empowers users to make informed decisions based on accurate data, leading to improved efficiency and resource management. With its ability to support thousands of devices within a wide coverage area, LoRaWAN stands out as a fundamental technology in the ongoing development of IoT solutions, ushering in a new era of connectivity and automation.
Key Features of LoRaWAN Sensors for Data Collection and Transmission
LoRaWAN sensors are designed with several key features that make them ideal for efficient data collection and transmission in IoT solutions. One of their most significant attributes is their long-range capability, allowing devices to communicate over distances that traditional sensors cannot cover. This is particularly valuable in applications such as smart cities or agricultural monitoring, where the distance between sensors and gateways can often be substantial. By leveraging low-frequency wireless communication, these sensors can transmit data effectively even in challenging environments, ensuring consistent connectivity and data flow.
Another important feature of LoRaWAN sensors is their low power consumption, which is crucial for the longevity of battery-operated devices. This attribute not only extends the operational life of the sensors but also reduces maintenance costs significantly. By utilizing a duty cycle that allows the sensors to remain inactive for most of the time, they conserve energy while still being capable of sending periodic updates. Furthermore, the ability to deploy a large number of sensors in a network allows for comprehensive data collection, enhancing the overall intelligence of IoT solutions while keeping resource usage minimal. Together, these features position LoRaWAN sensors as an efficient choice for organizations aiming to optimize their IoT implementations.
Analyzing Real-world Applications of LoRaWAN in Smart Cities
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) has emerged as a pivotal technology in the realm of IoT solutions, particularly in the development of smart cities. By leveraging its low-power, long-range capabilities, urban planners and municipalities can deploy sensors for a variety of applications, fundamentally transforming urban management. For instance, a report by the Global IoT Market Research forecasts that the adoption of LoRaWAN in smart cities will save municipalities up to 30% in operational costs by optimizing resource use and enhancing data collection efficiency.
Real-world applications of LoRaWAN sensors showcase its effectiveness in various domains such as smart waste management, air quality monitoring, and traffic management. According to a recent study, cities implementing smart waste solutions have seen a reduction in waste collection costs by 20-50%, as sensors can accurately monitor bin fill levels and optimize collection routes. Additionally, air quality sensors powered by LoRaWAN technology enable continuous monitoring of pollutants, providing critical data that informs public health initiatives and regulatory measures. The use of these sensors not only improves urban living conditions but also empowers citizens to make informed decisions about their environment.
The scalability of LoRaWAN is another vital aspect contributing to its adoption in smart cities. With the ability to support thousands of devices over long distances, it creates an optimal ecosystem for comprehensive urban data collection. As reported by market analysts, the number of connected LoRaWAN devices is expected to exceed 1 billion by 2025, underscoring the growing reliance on such technologies for urban development. Through effective integration of LoRaWAN sensors, cities can harness data to drive innovation and improve the quality of life for their inhabitants.
Evaluating the Cost-Benefit of Implementing LoRaWAN Solutions
When considering the implementation of LoRaWAN sensors for IoT solutions, evaluating the cost-benefit is crucial for making informed decisions. These sensors provide long-range communication capabilities with low power consumption, making them ideal for applications in agriculture, smart cities, and industrial monitoring. However, the initial investment in infrastructure and devices can be substantial, so it's important to analyze potential returns carefully. Factors such as reduced operational costs, improved data accuracy, and enhanced decision-making should be weighed against the deployment expenses.
**Tips:** One effective approach is to conduct a pilot program that allows you to test the LoRaWAN technology in a real-world scenario without a significant commitment. This can help identify specific use cases where the benefits outshine costs. Additionally, consider exploring community networks or partnerships that can share the infrastructure cost, thereby improving the overall ROI.
It's also vital to factor in the scalability of the solution. LoRaWAN's ability to support a large number of sensors makes it a great option for expanding operations over time. Businesses should assess their future needs and select solutions that can grow alongside their operations, ensuring that the initial investment continues to provide value in the long run.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Implementing LoRaWAN Sensors
This chart illustrates the cost-benefit analysis of implementing LoRaWAN sensors across different use cases. The data represents the estimated costs and potential savings associated with using LoRaWAN technology for various IoT solutions.
Best Practices for Integrating LoRaWAN Sensors into Existing Systems
Integrating LoRaWAN sensors into existing systems can significantly enhance the effectiveness of IoT solutions, especially in sectors like agriculture, smart cities, and logistics. According to a report from the GSMA, the global LoRaWAN market is set to grow at a CAGR of 17.6%, reaching $21 billion by 2025. To leverage this growth, organizations must follow best practices to ensure seamless integration with their current infrastructure.
One key practice is to conduct a thorough assessment of existing systems to identify compatibility with LoRaWAN technology. This includes evaluating data formats, communication protocols, and hardware requirements. Adopting a modular approach can facilitate the integration process by allowing organizations to incrementally implement LoRaWAN sensors, thus minimizing disruption to ongoing operations. A white paper from Statista indicates that businesses leveraging such modular strategies experience a 30% reduction in deployment costs compared to those opting for complete overhauls.
Additionally, ensuring robust data management systems is crucial for taking full advantage of the data provided by LoRaWAN sensors. With the influx of data, having a centralized platform for data analytics can assist in deriving actionable insights. The International Data Corporation (IDC) anticipates that by 2025, over 80% of organizations will integrate IoT data into their decision-making processes. This integration not only fosters better operational efficiencies but also enhances predictive maintenance capabilities, allowing organizations to preempt issues before they escalate.
How to Use LoRaWAN Sensors for Efficient IoT Solutions - Best Practices for Integrating LoRaWAN Sensors into Existing Systems
| Sensor Type | Application | Battery Life (Years) | Range (km) | Data Rate (bps) | Integration Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Sensor | Environmental Monitoring | 5 | 15 | 0.3 | Moderate |
| Soil Moisture Sensor | Agriculture | 3 | 10 | 0.5 | Low |
| Air Quality Sensor | Urban Monitoring | 4 | 7 | 1 | High |
| Water Level Sensor | Flood Monitoring | 6 | 12 | 0.5 | Moderate |
| Movement Sensor | Security | 2 | 5 | 50 | High |
Related Posts
-

Top 5 Data Loggers to Watch for in 2025 That Will Revolutionize Your Data Collection
-

Top 5 Power Monitoring Systems to Boost Energy Efficiency by 30% in 2023
-

2025 Top Power Monitors: Essential Tools for Energy Efficiency and Management
-
10 Essential Tips for Effective Tank Level Monitoring System Management
-

2025 Top 10 Data Loggers You Can't Miss: Ultimate Buying Guide
-

Why You Need a Power Consumption Meter to Save Energy and Reduce Costs

